Leave Your Message
A glass bottle is a common yet fascinating object. It holds liquids from beverages to essential oils. These bottles come in various shapes and sizes, appealing to both manufacturers and consumers. A glass bottle can evoke feelings of nostalgia, especially when associated with vintage sodas or homemade preserves.
One might wonder about the environmental impact of glass bottles. They can be recycled, reducing waste in landfills. However, the process requires energy, and not all bottles are recycled effectively. This raises questions about sustainability. Are we using glass bottles responsibly?
In cafes and homes, glass bottles enhance aesthetic appeal. They can be reused for storage or as decorative items. Yet, despite their beauty, they may not be the best choice for every situation. Their fragility can pose risks. Reflecting on our choices reveals the complexity of seemingly simple objects like a glass bottle.

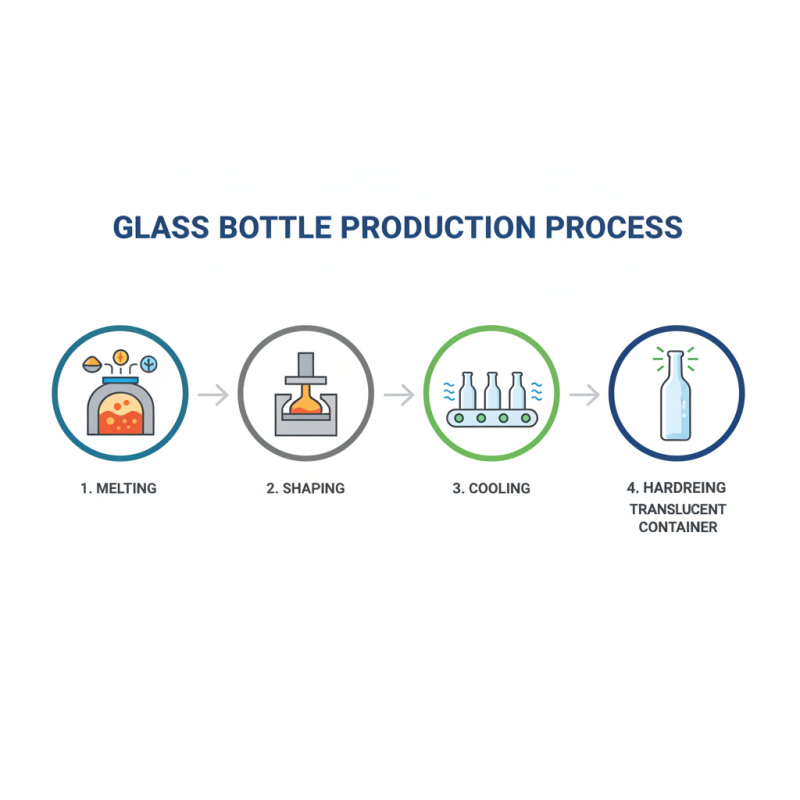
Glass bottles are remarkable containers made from silica, soda ash, and limestone. The process begins with heating these materials until they melt into a thick liquid. This molten glass is then carefully shaped into bottles using molds. Once cooled, the glass hardens, resulting in a sturdy, translucent container.
The composition of glass bottles contributes to their versatility. They are impermeable, which means they protect contents from air and moisture. This feature allows them to store beverages, sauces, and even cosmetics effectively. However, glass is fragile; it can break easily if dropped. This imperfection raises questions about safety and handling during transport and usage.
Recycling glass bottles is imperative for sustainability. While glass is endlessly recyclable, improper disposal remains a significant concern. Many people overlook how often they use glass bottles and the impact of waste. These issues invite reflection on our habits and encourage more environmentally-friendly choices in container use.
Glass bottles have a rich history in the packaging industry. They date back to around 1500 BC when ancient Egyptians crafted the first ones. Initially, their use was reserved for precious liquids. The development of glassblowing techniques in the 1st century AD allowed for mass production. As a result, glass bottles gained popularity across various cultures.
By the 19th century, the industrial revolution transformed glass bottle manufacturing. Mechanized production increased efficiency and reduced costs. Reports indicate that global glass packaging market growth is expected to reach $65 billion by 2027. This surge is driven by demand for sustainable and reusable packaging. Yet, challenges remain in recycling practices and environmental impact.
**Tip:** Always choose clear glass bottles for beverages. They provide better UV protection and prevent undesirable chemical reactions.
Today, glass bottles are versatile. They are used for beverages, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. However, they can be heavy and fragile. This makes transportation costs higher compared to plastic counterparts. Companies must consider these factors when choosing packaging.
**Tip:** Look for local recycling programs to help reduce waste. Proper disposal can promote sustainability.
Glass bottles are celebrated for their unique advantages over plastic. One major benefit is their durability. Unlike plastic, which can degrade over time, glass maintains its integrity for years. This longevity is appealing for consumers looking for reliable packaging. Additionally, glass is non-reactive and does not leach harmful chemicals into its contents. This property makes it a safer choice for food and beverages.
Another advantage is the environmental aspect. Glass is recyclable and can be reused endlessly without losing quality. While recycling options for plastic exist, the process often results in lower-grade materials. This creates a cycle of waste. In contrast, glass bottles can contribute to a more sustainable future. However, it’s worth reflecting on the energy-intensive processes required for glass production and recycling, which might offset some environmental benefits.
The aesthetic quality of glass also stands out. Many consumers appreciate the elegant look of glass bottles. They can elevate the presentation of drinks and food, making them more appealing overall. However, one must consider the weight of glass compared to plastic. Heavier bottles may not be as convenient for travel. Balancing these factors is essential when choosing the right packaging for various needs.
Glass bottles have diverse applications across many industries. In the food and beverage sector, they serve as a premium packaging option. According to a recent industry report, the global glass bottle market is projected to reach $90 billion by 2024. This growth reflects a rising consumer preference for sustainable packaging. Glass is recyclable and does not leach harmful chemicals, which appeals to eco-conscious buyers.
In the pharmaceutical industry, glass bottles protect sensitive medications. They prevent contamination and preserve drug efficacy. A study indicates that over 80% of pharmaceuticals are packaged in glass. This choice enhances product safety and maintains quality. For the cosmetics sector, glass provides an upscale feel. Many consumers associate glass with quality. This perception can drive higher sales.
Tips: Consider switching to glass bottles in your packaging strategy. They not only boost your brand image but also reduce environmental impact. However, think about logistics. Glass is heavier and can increase shipping costs. Weigh the pros and cons carefully. Be mindful of breakage during transit, which can lead to losses.
The global market for glass bottles is experiencing significant growth. Recent reports indicate an annual growth rate of around 4.5% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is largely driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly packaging. Consumers are becoming more aware of environmental issues. They prefer sustainable options like glass over plastics.
In 2022, the glass recycling rate reached 33% worldwide. This rate has improved, yet still leaves room for enhancement. Many regions struggle with recycling infrastructure. Some experts suggest that better collection methods could increase this percentage. Improving recycling systems can reduce raw material costs and energy usage in production.
The production of glass bottles also raises concerns. The process is energy-intensive, often relying on non-renewable resources. However, advancements in technology may help. Innovations in manufacturing can lower emissions and optimize energy consumption. While the industry shows promise, it still faces challenges that need addressing for true sustainability.
| Year | Global Production (Million units) | Recycling Rate (%) | Market Value (Billion USD) | Uses (% of Total) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 200 | 51 | 28.5 | 40 |
| 2020 | 210 | 52 | 29.1 | 42 |
| 2021 | 220 | 54 | 30.3 | 45 |
| 2022 | 230 | 55 | 31.2 | 46 |
| 2023 | 240 | 58 | 32.5 | 48 |